 |
 |
 |
   |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |


(NEW)鏡像スピーカーによるスマートフォン屋内位置認識システム
 |
|
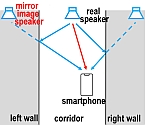
屋内位置認識における問題点の1つは、新たな機材導入による(労力、財政的)設置コストである。 本研究では、壁や床からの反射波を積極的に活用することでこの問題の解決を試みる。反射体に対し実スピーカと対称な位置に仮想的なスピーカ(鏡像スピーカ)を想定し、反射波を鏡像スピーカから発信されたと考えることで音源数を増やすことができる。これらの複数スピーカを用いた多辺測量(multi-lateration)により3次元測位が可能となる。 スマートフォンを用いた実験により、測位誤差の90th percentile値が5cm未満となることを確認した。提案手法は、利用可能なスピーカ数が少なく反射波が発生しやすい環境(例えば、オフィスビル内の廊下を対象とした訪問者ナビゲーションなど)での展開が期待される。
|
(NEW)反射光受信による可視光位置認識システム
 |
|
屋内照明を用いた位置認識システムでは、受信機で複数の照明光を直接受信できることを想定する場合が多い。しかし、通常の屋内空間では、照明装置が密に配置されているとは限らないため、この条件を満足することは難しい。そこで本研究では、反射光の強度を用いた屋内可視光位置認識システムを構築した。床にカメラを向けることで、複数の照明装置からの反射光を同時に取得できる。異なる照明装置から異なる周波数の変調光を送信し、取得された反射光の強度が照明装置からの距離に依存すること、それらの強度比から位置推定ができることを示した。スマートフォンカメラを用いたシステムを構築し、実証実験による性能評価を進めている。
|
汎用動画カメラを用いた高速高精度時刻同期技術
 |
|
社会への普及が進むLED照明とスマートフォン等に搭載される汎用動画カメラを用いた高速高精度時刻同期技術を提案する。
理論的解析を通して、カメラのシャッタースピードをパラメータとする最適変調照明についての数式表現を導出した。
1つのLED光源と60fpsのカメラを用いた実環境での評価実験では、観測時間0.067秒(4フレーム画像)で90 percentile誤差
26.3 μsを達成した。コンピュータシミュレーションによる比較実験では、
最適変調照明を用いることで時刻同期の計算量が抑えられることも明らかになった。
提案手法の特徴を利用したアプリケーションとして、高速可視光通信,(NEW)違法撮影判定,屋内位置認識,複数カメラ同期によるモーションキャプチャシステム等の実装を進めている。
|
ローリングシャッターカメラによる高速で選択的な可視光通信
 |
|
照明から送信される最適変調信号(上記参照)をカメラで受信することで、フリッカレスかつ高速な可視光通信を実現した。
60 fpsで1080本のラインセンサを持つ汎用動画カメラを用いた実験では最大で75 kbpsを達成し、従来のon-off keyingによる理論的限界を上回る性能を示すことを確認した。
さらに、OFDM変調されたマルチキャリア信号を用いた可視光通信の性能を理論的に解析した。また、露光時間による各キャリア波の受信感度の相違を利用することにより、
複数カメラに対する(NEW)選択的通信が可能であることを実証した。
|
 |
|
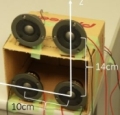
For rapid indoor 3D localization of smartphones, a new method called Frequency Division Multiplexing Phase Accordance Method (FDM-PAM) is proposed. The method uses a beat called a sync pattern composed of a pair of sinusoidal waves whose frequencies are slightly different, which is the same way as our original ultrasound ranging technique called the Phase Accordance Method (PAM). By generating multiple sync patterns whose central frequencies are different and transmitting each of them from different speakers, FDM-PAM conducts time-difference-of-arrival (TDOA) multilateration. In the current implementation of FDM-PAM, four sync patterns are generated by using two out of eight sinusoidal waves whose frequencies range from 14.75 kHz to 18.25 kHz (frequency interval: 500 Hz). Through experiments using four speakers in short baseline intervals (10-14 cm), it is confirmed that FDM-PAM achieves accuracy range around 10 to 30 centimeters using only a transmission of a short burst (4 ms), which indicates a sufficiently rapid indoor localization for smartphones.
|
Rapid Optical Ranging Technique
 |
|
The proposed optical ranging technique called LT-PAM (Long-Term Phase Accordance Method) transmits multiple sync patterns composed of two sinusoidal waves with different frequencies. Unlike chirp modulation techniques, LT-PAM transmits the two waves simultaneously and thus enables the shortening of measurement time. We have conducted experiments using two types of light sources, collimated and diffused light.
The experimental results indicated that the proposed method showed a moderate level of accuracy by adjusting the measurement time.
|
Compact 3D Tracking System
 |
|
We propose a novel technique for 3D localization that integrates a single camera and ultrasound. We use the Extended Phase Accordance Method and the ultrasound to measure accurately the distance to a moving target and we use the camera to identify the target’s 2D position on the image plane. A prototype system consists of a transmitter unit mounting one ultrasound transmitter and three infrared LEDs around it, and a receiver unit with one inexpensive camera and one ultrasound receiver. |
Ultrasound Motion Capture System
 |
|
We propose an innovative motion capture system using ultrasonic communications. Compared with existing commercial motion-capture systems that use optical or magnetic sensing, the proposed system can provide a cost effective solution for industrial and entertainment applications. To improve the capture rate of the proposed system, the EPAM algorithm was implemented in a field-programmable gate array (FPGA). |
 |
|
複数のユーザ間の相対的な位置データを、超音波通信を用いて取得する研究です。近年では、モバイルデバイスの普及が急速に進んでいるため、本研究はモバイ ルデバイス向けに実装を進めています。従来の位置認識手法よりも高精度の測定が、外部の機器を必要とせずに実現可能です。本技術が実装されれば、様々なア プリケーションに応用できると考えています。 |
|
 |
 |
 |
|

