床面反射光による屋内ドローントラッキング
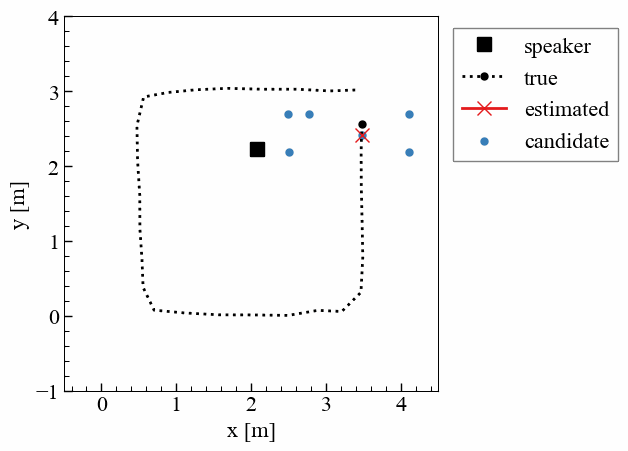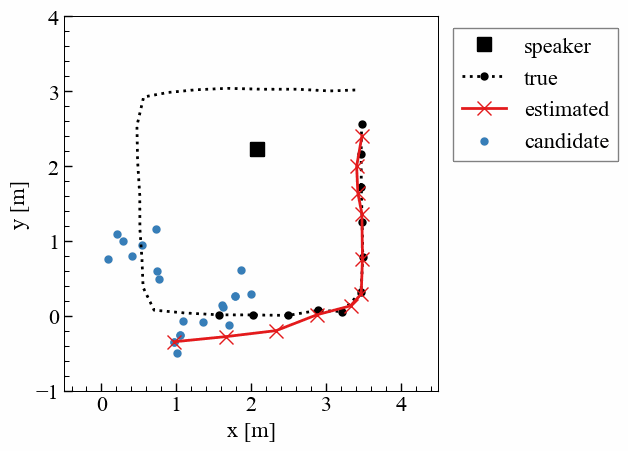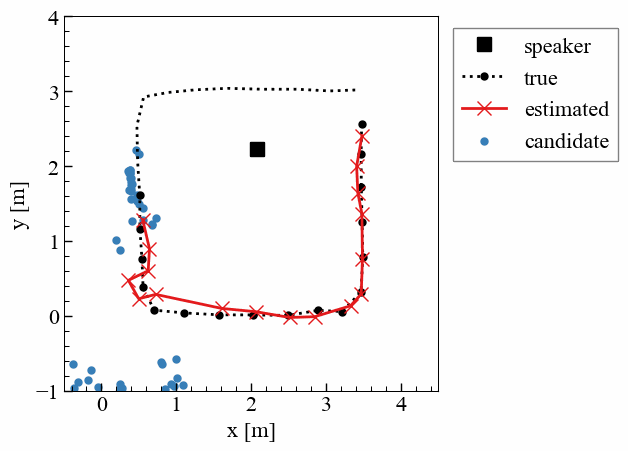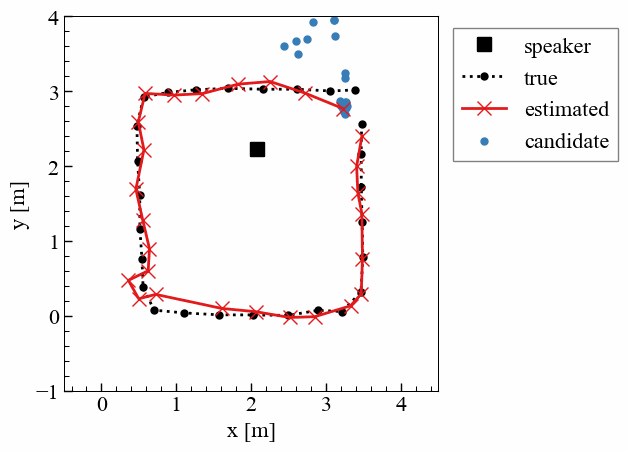
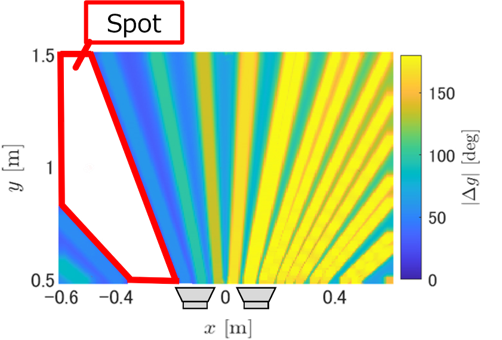
屋内でのドローン活用は、物流や点検、警備など幅広い分野で期待されている。しかし、屋内では衛星測位(GNSS)が利用できないため,実用における高精度な位置推定技術が不可欠である。本研究では、天井の複数のLED照明を異なる周波数で点滅させ、その光が床で反射した「床面反射光」をドローン搭載カメラで撮影し、位置を推定する手法を提案している。カメラの撮像特性を利用して照明ごとの光を画像上で分離し、1枚の画像から三次元的な位置を算出できる点が特徴である。実験により、30cm程度の精度で位置を推定可能であることを確認した。
Paper:
・Onishi, Y., Watanabe, H., Nakamura, M., Hashizume, H., Sugimoto, M.: Indoor Drone 3D Tracking Using Reflected Light from Floor Surfaces, IEEE Journal of Indoor Positioning and Navigation, vol. 2, pp. 251-262, 2024 (doi: 10.1109/JISPIN.2024.3453775).
・大西,渡邉,中村,橋爪,杉本:床面反射光を用いることによる屋内ドローントラッキング,情報処理学会論文誌, Vol. 64, No. 11, pp.1576-1587 (2023).